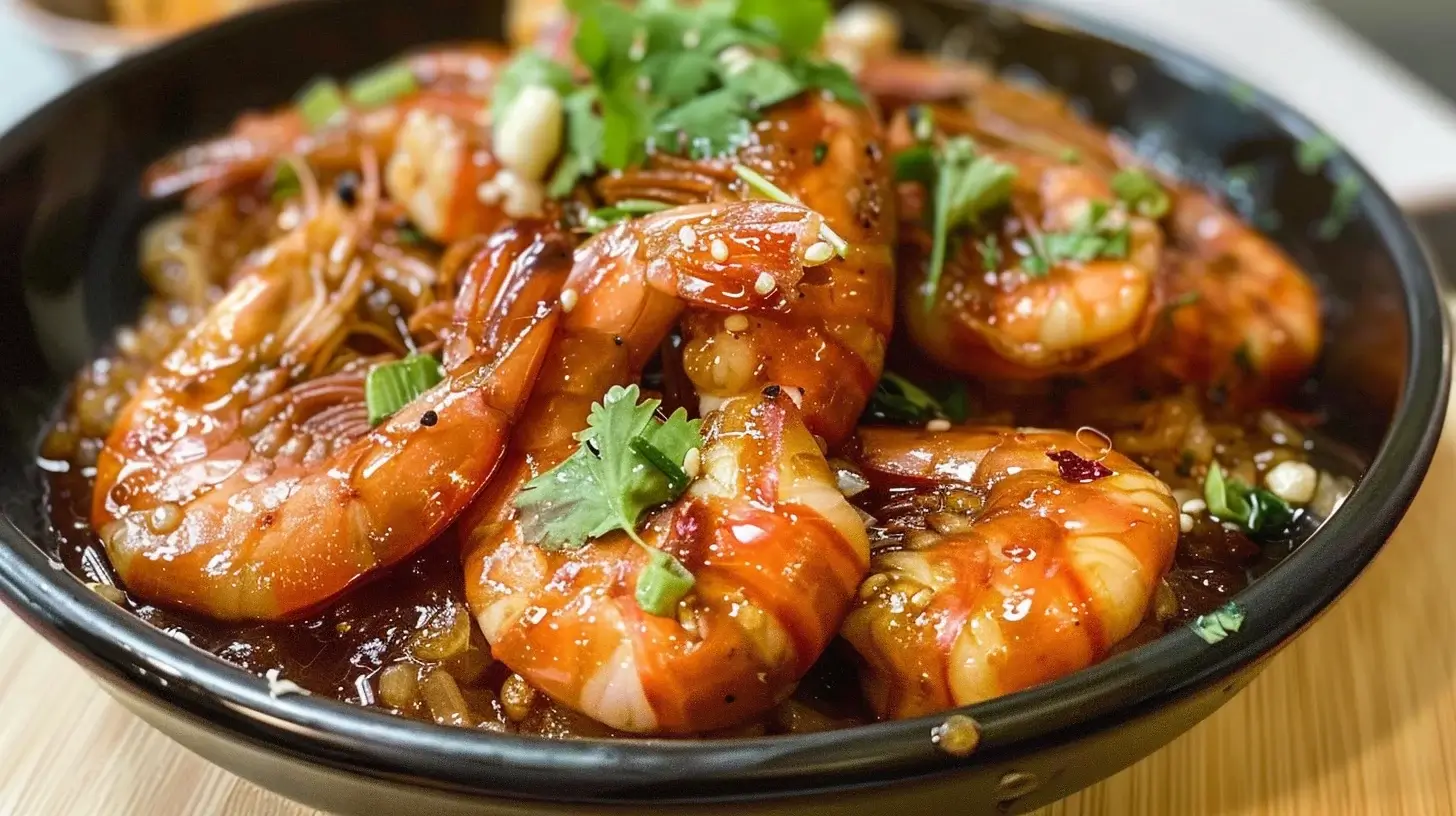
Tiger shrimp are a popular and sought-after species of shrimp, known for their distinctive striped appearance and sweet, firm texture. These crustaceans are commonly found in both wild and farmed environments, and their unique characteristics make them a staple in various culinary dishes worldwide. Whether you’re a seafood enthusiast or simply exploring new ingredients for your meals, understanding the nature of tiger shrimp will deepen your appreciation for this versatile delicacy.
What Are Tiger Shrimp?
Tiger shrimp, scientifically known as Penaeus monodon, are large-sized shrimp primarily found in the Indo-Pacific region, but they are also cultivated in other parts of the world. They are distinguished by their striking black and white striped shells, which resemble the pattern of a tiger’s coat. These shrimp are highly valued for their sweet, succulent meat and are commonly used in many seafood dishes, including stir-fries, curries, and grilled preparations.

History and Origins of Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp have been an important part of the fishing and aquaculture industries for centuries. Originating in the coastal waters of Southeast Asia, their commercial farming began in the late 20th century and spread to other regions. Their ability to grow quickly and adapt to various environments made them an attractive choice for aquaculture operations. As a result, tiger shrimp farming expanded globally, and they are now produced in countries such as Thailand, India, Indonesia, and even the United States.
How Tiger Shrimp Differ from Other Shrimp Varieties
Tiger shrimp stand out from other shrimp varieties due to their large size and distinctive appearance. Unlike smaller shrimp, tiger shrimp can grow up to 13 inches long. Their shells are covered with black and white stripes, setting them apart from other shrimp species that often have a more uniform color. Furthermore, tiger shrimp are known for their firm, sweet, and delicate meat, which makes them ideal for a variety of culinary applications. In comparison to smaller shrimp, such as white or brown shrimp, tiger shrimp offer a more substantial bite and a richer flavor.
Tiger Shrimp Biology and Anatomy
Physical Characteristics of Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp have several unique physical characteristics that contribute to their signature appearance. Their hard exoskeleton features a pattern of black and white stripes, which provides camouflage in the wild. Their long, slender bodies are equipped with ten legs, a pair of long antennae, and large claws. The body of the shrimp is divided into segments, with a muscular abdomen and tail that helps them swim rapidly through the water.
Lifespan and Growth Stages
Tiger shrimp have a relatively short lifespan, typically ranging from 2 to 3 years in the wild. They undergo several growth stages, beginning as larvae, followed by juvenile and adult stages. They are fast-growing creatures, reaching harvest size in about 6 to 8 months in aquaculture settings. As they mature, they molt their exoskeleton multiple times, growing larger with each molt until they reach their full adult size.
Habitat and Distribution of Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp are typically found in tropical and subtropical waters, especially in the coastal regions of Southeast Asia, Australia, and parts of the Indian Ocean. They prefer shallow, warm waters and are often found in estuaries, mangrove forests, and brackish lagoons. In addition to wild populations, tiger shrimp are commonly farmed in controlled environments like ponds and tanks, where conditions can be optimized for their growth and reproduction.
Nutritional Value of Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp are not only delicious but also offer a range of nutritional benefits. As a low-calorie and high-protein food, they make an excellent addition to a balanced diet. Rich in essential nutrients, they are a great source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and several important vitamins and minerals.
Protein Content and Other Nutrients
Tiger shrimp are known for their high protein content, which provides the body with essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth, repair, and overall health. A typical serving of tiger shrimp (3 ounces) contains around 18 grams of protein. Additionally, they are rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, phosphorus, iodine, and selenium. These nutrients play key roles in supporting metabolism, bone health, and immune function.
Health Benefits of Eating Tiger Shrimp
Consuming tiger shrimp offers various health benefits. Their high protein content supports muscle building and repair, while their omega-3 fatty acids contribute to heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering cholesterol levels. Moreover, the selenium found in tiger shrimp has antioxidant properties that help protect cells from damage. Tiger shrimp are also low in fat, making them a great option for individuals looking to maintain a healthy weight or reduce their fat intake.
Commercial Importance of Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp play a significant role in the global shrimp industry, contributing to both wild capture fisheries and aquaculture sectors. Their large size, distinct appearance, and delicious taste make them a highly sought-after product in markets around the world. As a result, tiger shrimp farming has become a major component of the seafood industry, driving economies in countries with shrimp farming operations.
The Global Shrimp Industry and Tiger Shrimp’s Role
The shrimp industry is a multi-billion-dollar market, with tiger shrimp making up a substantial portion of global shrimp production. In countries like Thailand, India, and Indonesia, tiger shrimp farming is a key economic driver, providing jobs and supporting local economies. Due to their fast growth and large size, tiger shrimp are particularly valuable in international trade, where they are exported to countries around the world. Their high demand in restaurants and retail markets ensures their continued importance in the seafood industry.
Environmental Impact and Sustainable Farming Practices
While tiger shrimp farming has grown significantly, it has also raised environmental concerns, particularly regarding the impact on coastal ecosystems and the use of resources. Traditional shrimp farming practices, such as clear-cutting mangrove forests to create shrimp ponds, have led to habitat loss and biodiversity decline. However, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices, such as implementing recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), improving pond management techniques, and restoring mangrove habitats. These practices aim to reduce environmental damage while maintaining the economic viability of shrimp farming.
How to Harvest and Farm Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp farming and harvesting require specific knowledge and skills to ensure a high-quality and sustainable yield. Farmers must carefully manage water quality, feed, and the overall environment to optimize shrimp growth and health.
The Process of Harvesting Tiger Shrimp
The process of harvesting tiger shrimp involves monitoring their growth and determining the optimal time for harvest. Typically, shrimp are harvested once they reach a marketable size, which usually takes 6 to 8 months in farmed environments. Harvesting is often done manually, with workers using nets or traps to collect the shrimp from ponds or tanks. After being harvested, the shrimp are immediately transported to processing facilities where they are cleaned, sorted, and prepared for distribution.
Methods of Farming Tiger Shrimp for Commercial Use
Commercial tiger shrimp farming involves creating controlled environments where shrimp can grow efficiently and without the risks posed by the open ocean. These farms typically use ponds, tanks, or other artificial structures to cultivate shrimp. In intensive farming systems, high-density stocking is used, meaning a large number of shrimp are placed in relatively small areas to maximize production. Other methods, such as organic farming, focus on reducing the use of chemicals and antibiotics in favor of more natural approaches. Successful tiger shrimp farming requires careful monitoring of water quality, temperature, salinity, and oxygen levels to ensure the shrimp remain healthy throughout their growth cycle.
Cooking with Tiger Shrimp
Tiger shrimp are not only an important commercial product but also a culinary delight, offering a sweet and firm texture that makes them ideal for a variety of dishes. They can be cooked in countless ways, from grilling and boiling to stir-frying and sautéing. Their versatility and delicious flavor make them a favorite among chefs and home cooks alike.
Popular Recipes Featuring Tiger Shrimp
There are many ways to enjoy tiger shrimp, with several popular recipes that highlight their natural flavor. Some of the most well-known dishes include:
- Garlic Butter Tiger Shrimp: Shrimp sautéed in a rich and flavorful garlic butter sauce, often served over pasta or with crusty bread.
- Shrimp Tacos: A light and flavorful option, tiger shrimp can be grilled or sautéed and placed in soft tortillas with a variety of fresh toppings like avocado, salsa, and cabbage.
- Tiger Shrimp Stir-Fry: Stir-fried with vegetables and a savory sauce, this dish is both healthy and satisfying.
- Tiger Shrimp Scampi: A classic Italian dish with shrimp cooked in garlic, butter, and white wine, served over pasta.
- Cajun-Spiced Tiger Shrimp: Shrimp seasoned with bold Cajun spices and either grilled or pan-seared for a flavorful and zesty dish.
How to Cook Tiger Shrimp Perfectly Every Time
Cooking tiger shrimp to perfection is simple once you know a few key techniques. Here are some tips to ensure your shrimp come out delicious every time:
- Don’t Overcook: Tiger shrimp cook quickly, typically in just 2 to 3 minutes per side. Overcooking can make them tough and rubbery, so be sure to keep an eye on them as they cook.
- Use High Heat: Whether grilling, sautéing, or stir-frying, cooking at high heat helps to develop a nice sear and preserve the shrimp’s juicy texture.
- Peel and Devein: For most recipes, it’s best to peel and devein the shrimp before cooking. This not only improves their appearance but also enhances the texture.
- Marinate for Extra Flavor: If you want to elevate the flavor, marinate tiger shrimp for 15 to 30 minutes before cooking. Use a mixture of olive oil, lemon juice, garlic, and your favorite herbs for a simple yet tasty marinade.
- Watch for Color Change: When cooking tiger shrimp, they will turn from translucent to a pinkish-orange color. Once they’ve turned opaque, they’re ready to be served.
With these tips in mind, you’ll be able to enjoy perfectly cooked tiger shrimp in any dish you choose.
Economic Impact of Tiger Shrimp Farming
Tiger shrimp farming has become a significant economic activity in many countries, particularly those in Southeast Asia and Latin America. The industry supports thousands of jobs and contributes to local and national economies, both through direct employment and the production of a globally traded commodity. However, the economic benefits come with challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable growth.
Employment and Income Generation in Tiger Shrimp Farming Regions
In regions where tiger shrimp farming is prevalent, the industry plays a crucial role in providing employment and generating income for local communities. The farming of tiger shrimp creates jobs at various stages, including in hatcheries, farms, processing plants, and distribution networks. This has led to economic growth in rural and coastal areas, where opportunities for alternative industries may be limited. Furthermore, the industry supports ancillary sectors, such as transportation, packaging, and retail, creating a ripple effect of economic activity. The income generated from tiger shrimp farming is vital for many households, helping to improve the standard of living in these areas.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Tiger Shrimp Farming
While tiger shrimp farming presents significant economic opportunities, it is also fraught with challenges. One of the key difficulties is managing disease outbreaks, which can devastate shrimp populations and disrupt production. Additionally, the need for large quantities of land and water can strain local resources, particularly in regions already facing environmental pressures. However, opportunities exist in the form of new farming techniques, including the adoption of more sustainable practices and the development of disease-resistant shrimp strains. Additionally, there is potential for growth in organic and ethically farmed tiger shrimp markets, which cater to environmentally conscious consumers.
Environmental Concerns Regarding Tiger Shrimp
The environmental impact of tiger shrimp farming is a major concern, particularly in relation to the destruction of natural habitats and the degradation of water quality. While shrimp farming can be highly profitable, it also poses risks to local ecosystems if not managed responsibly.
Effects on Marine Ecosystems
The expansion of tiger shrimp farming has led to significant environmental changes, especially in coastal areas where mangrove forests and wetlands are cleared to make way for shrimp ponds. The loss of these critical habitats can disrupt local wildlife, reduce biodiversity, and alter ecosystems. Furthermore, the release of untreated wastewater from shrimp farms can pollute surrounding water sources, affecting marine life and water quality. The use of chemicals, such as antibiotics and pesticides, in shrimp farming can also have detrimental effects on the environment, potentially contaminating surrounding ecosystems and harming other species.
Addressing Environmental Issues in Tiger Shrimp Farming
To address the environmental concerns associated with tiger shrimp farming, many producers are adopting more sustainable farming practices. One approach is the establishment of shrimp farms that minimize habitat destruction, such as integrated mangrove-shrimp farming systems, which combine shrimp farming with the restoration of mangrove ecosystems. Additionally, water management practices, such as recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), help to reduce water usage and limit the pollution of surrounding areas. Implementing stricter regulations on chemical use and encouraging the use of eco-friendly alternatives are also key steps in reducing the environmental footprint of tiger shrimp farming.
Sustainability of Tiger Shrimp Farming
Sustainability in tiger shrimp farming is crucial for the long-term viability of the industry. It involves finding ways to meet market demand while minimizing environmental impact and ensuring social responsibility.
Best Practices for Sustainable Farming
Sustainable tiger shrimp farming practices include optimizing feed use, reducing chemical inputs, and managing water quality effectively. Using high-quality, sustainable feed reduces waste and ensures that shrimp are nourished with minimal environmental impact. Additionally, farming practices that emphasize water conservation, such as closed-loop systems, can help preserve valuable freshwater resources. Integrated farming systems that combine shrimp production with other agricultural activities, such as rice farming or algae cultivation, offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional farming methods. Promoting biodiversity within shrimp farms and enhancing the natural ecosystems can also improve sustainability.
Certifications and Ethical Farming Practices for Tiger Shrimp
There is growing demand for ethically farmed and certified tiger shrimp, particularly from environmentally conscious consumers. Certifications such as the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) ensure that farms meet high standards for environmental and social responsibility. These certifications focus on reducing the environmental impact of shrimp farming, improving animal welfare, and ensuring fair labor practices. As consumer awareness of sustainability issues grows, the demand for certified tiger shrimp is expected to increase, encouraging more farms to adopt ethical practices and sustainable methods.
Tiger Shrimp and Global Trade
Tiger shrimp are a valuable commodity in global trade, with millions of tons exported each year. As the demand for shrimp continues to grow, tiger shrimp play a key role in the seafood supply chain, contributing to the global economy and international relations.
Tiger Shrimp as an Export Commodity
Tiger shrimp are one of the most traded seafood products worldwide, with major exporting countries including Thailand, India, Indonesia, and Ecuador. These shrimp are highly sought after for their large size, sweet flavor, and versatility in various cuisines. They are exported in various forms, including fresh, frozen, and processed, to markets in the United States, Europe, Japan, and other regions. The global demand for tiger shrimp continues to rise, driven by their popularity in both high-end restaurants and everyday meals. This export market has helped to drive the growth of shrimp farming industries in producing countries, making tiger shrimp an essential global commodity.
Trade Barriers and Economic Effects on Tiger Shrimp Exporters
While the tiger shrimp trade brings significant economic benefits to exporting countries, it is also subject to trade barriers and regulations that can affect the flow of goods. Tariffs, import restrictions, and health regulations can create challenges for exporters, particularly when it comes to accessing high-demand markets. For example, countries may impose sanitary or phytosanitary measures to ensure that imported shrimp are safe for consumption, which can result in delays, additional costs, and market access limitations. Moreover, fluctuations in international trade policies, such as trade wars or changes in import duties, can impact the economic stability of tiger shrimp exporters. Despite these challenges, the global trade of tiger shrimp remains a significant contributor to the economies of producing nations, highlighting the importance of the industry in international commerce.
Tiger Shrimp in Popular Culture
Tiger shrimp have made their way into popular culture, especially in the culinary world, where they are admired for their distinct appearance and unique flavor. From fine dining restaurants to home kitchens, tiger shrimp are an important part of global cuisine and have even been referenced in various forms of media.
Tiger Shrimp in Culinary Traditions Worldwide
Tiger shrimp are used in a wide range of culinary traditions across the globe. In Southeast Asia, they are commonly featured in dishes like Thai shrimp curry and Vietnamese seafood soups. In Latin America, tiger shrimp are often incorporated into ceviche, a fresh, tangy dish popular in coastal regions. Meanwhile, in Western cuisine, tiger shrimp are frequently grilled, sautéed, or served in pasta dishes. The shrimp’s firm texture and sweet flavor make it a versatile ingredient, fitting into both spicy and mild dishes. Across the world, tiger shrimp are enjoyed for their distinct taste, elevating many regional specialties.
Representations of Tiger Shrimp in Media and Art
Tiger shrimp have also been depicted in various forms of art and media. They are often featured in food photography, advertisements, and cooking shows due to their striking appearance and appeal to seafood lovers. In visual art, tiger shrimp sometimes appear as symbols of luxury or exotic cuisine. They have been depicted in various styles, from hyper-realistic depictions to abstract interpretations, often symbolizing abundance and the beauty of marine life. Their prominence in these creative fields underscores their cultural significance as a high-end, desirable food product.
Tiger Shrimp vs Other Shrimp Varieties
When comparing tiger shrimp to other shrimp varieties, differences in taste, size, and texture become clear. These variations can influence which shrimp is ideal for certain recipes.
Taste, Size, and Texture Differences
Tiger shrimp are known for their larger size and firm texture compared to other shrimp varieties. While smaller shrimp, like white or brown shrimp, tend to have a more delicate texture, tiger shrimp are meatier and provide a more substantial bite. In terms of flavor, tiger shrimp are slightly sweeter, with a rich, slightly briny taste that makes them ideal for grilling, sautéing, or serving in seafood pasta. In contrast, smaller shrimp varieties often have a milder flavor and are commonly used in dishes like shrimp cocktails or shrimp salads.
Which Shrimp Variety Is Better for Specific Recipes?
The choice of shrimp variety depends on the dish you are preparing. Tiger shrimp’s firm texture and larger size make them perfect for grilling or skewering, as well as for dishes that highlight the shrimp as the main protein, such as shrimp scampi or stir-fry. Smaller shrimp varieties, like pink or white shrimp, are better suited for recipes that require quick cooking and smaller bites, such as shrimp cocktails, soups, or shrimp salads. Additionally, for recipes that need shrimp to blend into the background, such as in dumplings or pies, smaller shrimp might be the better choice.
Future of Tiger Shrimp Farming
The future of tiger shrimp farming is set to be shaped by technological innovations and the ongoing evolution of the global shrimp market. Advances in shrimp farming practices will focus on improving sustainability, increasing efficiency, and addressing the growing demand for shrimp.
Innovations in Shrimp Farming Technology
Technological advancements in shrimp farming are already making a significant impact on the industry. Innovations such as recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) allow shrimp farms to reduce water consumption and minimize environmental pollution. Additionally, genetic research is leading to the development of disease-resistant shrimp strains, which will help farmers reduce the use of antibiotics and maintain healthier stocks. Advances in automation, such as the use of drones for monitoring water quality and shrimp health, are also enhancing efficiency and productivity in shrimp farms. These technologies promise to make tiger shrimp farming more sustainable and cost-effective in the future.
The Future of Tiger Shrimp in Global Markets
The global demand for tiger shrimp is expected to continue growing as more consumers seek out high-quality, flavorful seafood. In particular, the rise of health-conscious eating habits and interest in protein-rich foods will drive demand for shrimp in general. However, the industry will need to balance this demand with sustainability concerns, particularly in terms of environmental impact and ethical farming practices. As consumer awareness of sustainability issues increases, the future of tiger shrimp will likely involve a greater focus on certified sustainable farming practices and ethical sourcing. The continued growth of international trade in tiger shrimp will also drive the development of new markets, particularly in emerging economies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best way to cook tiger shrimp?
The best way to cook tiger shrimp depends on your preferences, but popular methods include grilling, sautéing, and boiling. For grilling, marinate the shrimp in a flavorful mixture (like garlic, lemon, and olive oil) and cook them on high heat for 2-3 minutes per side. Sautéing in a pan with butter and garlic also brings out their sweet flavor, while boiling is ideal for making shrimp cocktails. Regardless of the method, ensure not to overcook the shrimp to maintain their tender, juicy texture.
Are tiger shrimp sustainable to farm?
Tiger shrimp farming can be sustainable if done responsibly. Farms that use recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), implement efficient water management practices, and avoid harmful chemicals help reduce environmental impact. Certifications from organizations like the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) can help consumers identify sustainably farmed shrimp. However, traditional shrimp farming practices, such as clearing mangrove forests for shrimp ponds, have led to significant environmental concerns, so it is important for farms to adopt more sustainable methods.
What makes tiger shrimp different from other shrimp?
Tiger shrimp are distinguished by their large size, firm texture, and distinctive black-and-white striped shell. Compared to smaller shrimp varieties, tiger shrimp are meatier, sweeter, and provide a more substantial bite. These qualities make them ideal for grilling, skewering, or other methods where the shrimp can be the main focus of a dish.
Can you farm tiger shrimp in freshwater?
Tiger shrimp are typically farmed in brackish water, which is a mix of saltwater and freshwater, rather than pure freshwater. They require the specific salinity levels found in coastal regions for optimal growth. While it is possible to farm them in controlled environments with adjusted salinity, farming them in pure freshwater is not ideal.
What is the lifespan of a tiger shrimp?
Tiger shrimp typically have a lifespan of 2 to 3 years in the wild, though their life expectancy can be shorter in farmed environments due to the intensive farming methods used to speed up production. During their lifespan, tiger shrimp undergo several growth stages, from larvae to juvenile to adult, molting several times before reaching maturity.
Are there any health risks associated with eating tiger shrimp?
Generally, tiger shrimp are safe to eat and provide numerous health benefits, including being rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, like all seafood, they can pose health risks if not properly handled or cooked, such as the risk of foodborne illness from undercooking or cross-contamination. Additionally, some people may have shellfish allergies, which can cause severe reactions. It is important to ensure that shrimp is sourced from reputable farms to avoid the potential for contamination with chemicals or antibiotics.